In recent years, there has been a shift in the global power structure. The traditional western powers are no longer the only dominant players in the world. The rise of the BRICS nations (Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa) has challenged the Western world’s supremacy and offered an alternative world order.
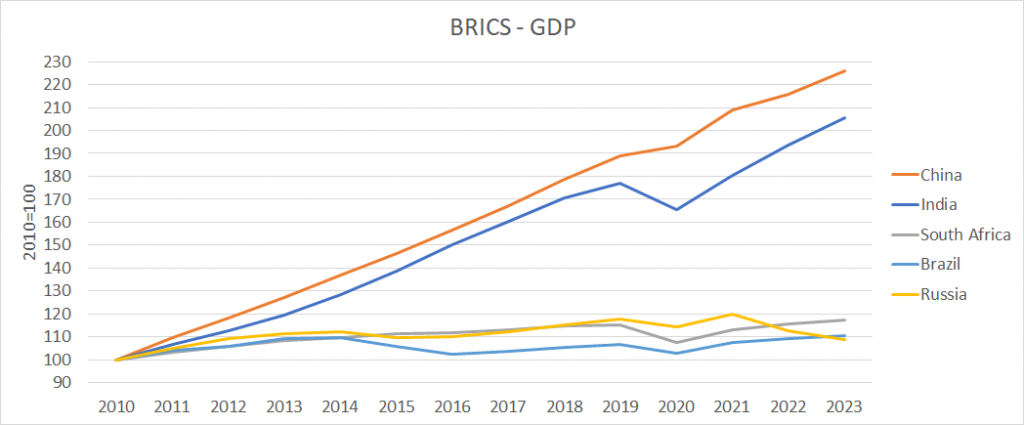
The BRICS nations represent over 40% of the world’s population and have a combined GDP of over $16 trillion. These nations are growing rapidly and have been responsible for a significant portion of global economic growth over the past decade. They have also established their own development bank and are working towards increasing their cooperation and influence on the global stage.
BRICS vs. the West
The BRICS nations have been challenging the dominance of the Western world by promoting a multipolar world order. They argue that the traditional Western powers have had too much influence in international organizations such as the World Bank and the International Monetary Fund (IMF). The BRICS nations believe that these organizations are biased towards the Western world and do not adequately represent the interests of developing nations.

To counter this, the BRICS nations established the New Development Bank (NDB) in 2014. The NDB is a development bank that is focused on infrastructure and sustainable development projects in developing nations. The bank is seen as an alternative to the World Bank and the IMF and is intended to provide developing nations with an alternative source of funding for their development projects.

The BRICS nations have also been promoting their own currencies as an alternative to the US dollar. They argue that the dominance of the US dollar in international trade has given the US too much power and has created an unfair advantage for the US. The BRICS nations believe that using their own currencies in international trade will increase their influence and reduce their reliance on the US.
Implications for the Global Economy
The rise of the BRICS nations has significant implications for the global economy. The shift towards a multipolar world order will lead to a more balanced distribution of power and influence. The dominance of the traditional Western powers will be challenged, and developing nations will have a greater say in international organizations.

The establishment of the NDB will also provide developing nations with an alternative source of funding for their development projects. This will reduce their reliance on the World Bank and the IMF and give them more control over their own development priorities.
The increased use of BRICS currencies in international trade will also have implications for the global economy. The US dollar has been the dominant currency in international trade for decades, but this is starting to change. As more countries use BRICS currencies in international trade, the US dollar’s dominance will decrease, and the influence of the BRICS nations will increase.
Challenges Facing the BRICS Nations
Despite their rapid economic growth and increasing influence, the BRICS nations still face significant challenges. Corruption, inequality, and political instability are significant challenges in many of these countries. These challenges could hinder their development and limit their ability to challenge the dominance of the Western world.
The COVID-19 pandemic has also had a significant impact on the BRICS nations. The pandemic has highlighted the vulnerability of these economies to external shocks and has led to a significant economic downturn in many of these countries.
Conclusion
The rise of the BRICS nations is a significant development in the global power structure. The shift towards a multipolar world order will lead to a more balanced distribution of power and influence. The BRICS nations are challenging the dominance of the Western world and offering an alternative world order.
The establishment of the NDB and the increased use of BRICS currencies in international trade are significant developments that will have implications for the global economy. However, the BRICS nations still face significant challenges, and their ability to challenge the dominance of the Western world will depend on how well they address these challenges.

Corruption, inequality, and political instability are significant challenges facing the BRICS nations. To address these challenges, these countries need to strengthen their institutions, promote transparency and accountability, and invest in human capital development. Without addressing these challenges, the BRICS nations’ potential to challenge the traditional Western powers will be limited.
The COVID-19 pandemic has also highlighted the vulnerability of these economies to external shocks. The pandemic has led to significant economic downturns in many of these countries, with millions of people losing their jobs and livelihoods. To recover from the pandemic, the BRICS nations need to focus on investing in their healthcare systems, supporting their vulnerable populations, and promoting economic growth.
In conclusion, the rise of the BRICS nations is a significant development in the global power structure. These countries represent a significant portion of the world’s population and have a combined GDP of over $16 trillion. The establishment of the NDB and the increased use of BRICS currencies in international trade are significant developments that will have implications for the global economy.

However, the BRICS nations still face significant challenges, and their ability to challenge the traditional Western powers will depend on how well they address these challenges. Corruption, inequality, and political instability are significant challenges that need to be addressed, and the COVID-19 pandemic has highlighted the vulnerability of these economies to external shocks.
As the world becomes more multipolar, it is important for the BRICS nations to work towards promoting a more balanced distribution of power and influence. By addressing their internal challenges and working together, the BRICS nations can establish themselves as a significant force in the global power structure, offering an alternative world order to the traditional Western powers.


